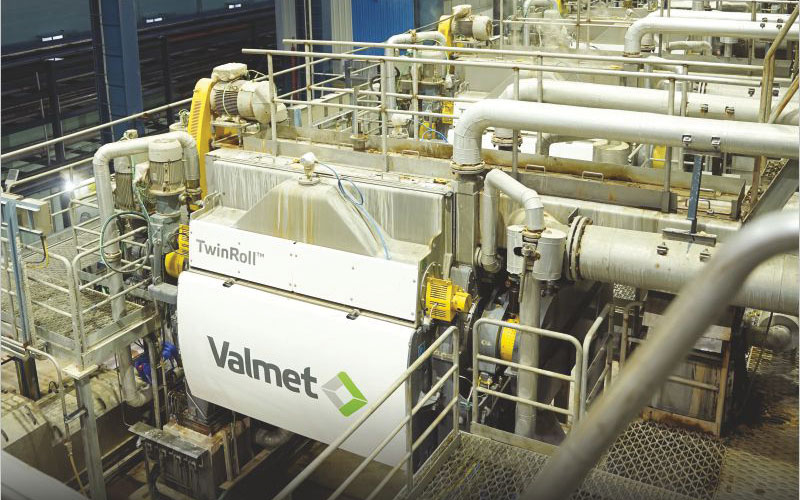

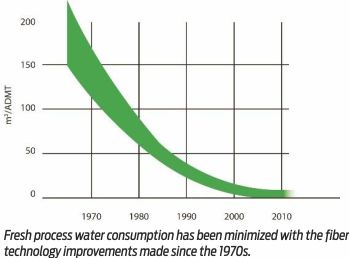
In the 70s, in a fiber line, the screening, brown stock washing, and bleaching processes were open during chemical pulp production, and the water went from there directly into the sewer. Since then technology has advanced enormously, use of TwinRoll presses has brought down freshwater consumption of between 150 and 200 m3 per air-dried tonne (ADMT) to today’s consumption of below 20 m3/ADMT in chemical pulp production.

Water Consumption Improvements in Fiber Lines
In a fiber line during the 1970s, the screening, brown stock washing, and bleaching processes were open during chemical pulp production, and the water went from there directly into the sewer. In the 1980s, brown stock washing was closed, reducing some of the emissions. During the 1990s, the bleaching process was closed, and the filters were to some extent replaced by presses in the brown stock washing. At the beginning of 2000, both brown stock washing and the bleaching process were press-based and closed systems, significantly reducing water use. For cooling, cooling towers were also used instead of an open system. Today, TwinRoll presses are used in both brown stock washing and bleaching, and the process water is recirculated throughout the fiber line, which greatly minimizes water consumption. Technology has advanced enormously since the 1970s, from a freshwater consumption of between 150 and 200 m3 per air-dried tonne (ADMT) to today’s consumption of below 20 m3/ADMT in chemical pulp production. Customers with an older fiber line thus have great opportunities to considerably reduce their water consumption.
Watch: Top Paper Companies 2023
Water Reduction Measures
Several water reduction measures are included when designing a new pulp or paper mill. For example, an important thing to do to reduce water consumption in a pulp mill is to use presses in the fiber line, which reduces effluent volumes. It is also important to produce evaporation condensate that is so clean it can be 100 percent reused in the process and to avoid an unnecessary internal cooling system. Keeping the cooling and process water separate requires less chemical-treated water and leads to less spillage. The cooling system setup depends on location and has a large impact on the water footprint. In cases where an open cooling system is used, the water is fed into and out of the mill without being polluted: It is just a little warmer when it leaves the mill.
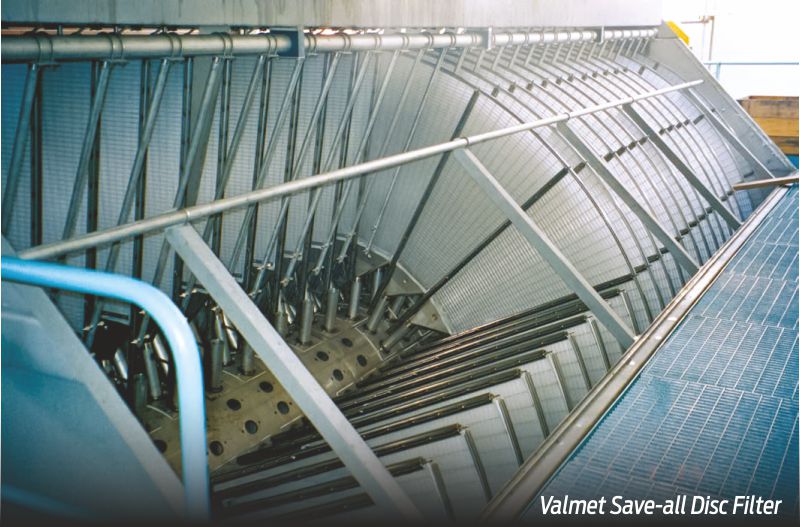
Valmet’s portfolio includes water treatment and dewatering technologies. Fiber and water are recovered in long circulation systems using Save-all disc filters. In a paper machine’s water loop, ultrafiltration is also used to clean clear filtrate after the disc filters and reduce freshwater consumption by removing bacteria, microstickies, colloids, and solids. Microflotation units are used in paper machines’ long water loop for sticky removal from press waters.
Valmet offers equipment and partners’ equipment the possibility of operating without water or with reduced water use. For example, nonflow mechanical seals and vacuum blower systems are technologies with zero effluent.
Another example is the Valmet Stock Mixer, which allows the mixing of chemical solutions without the use of freshwater, and Valmet’s Starch Cooking Unit, which operates without wasting water for cleaning and transition periods. Valmet’s filter fabric for twin wire and belt presses has good runnability and ensures efficient filtration.
Water recovery from air systems is among our solutions for pulp and paper mills. Valmet’s OptiAir Recovery mist remediation technology enables the reduction and elimination of odors, air pollution, and discharged moisture. It also enables the increase of heat recovery capacity and up to 70 percent water recovery from the exhaust air. Valmet offers suction roll seal upgrades that can reduce water consumption by between 50 and 85 percent.
Water Footprint Reduction in India
Valmet’s latest deliveries to factories in India meet today’s tough small water footprint demands. For example, a Kashipur mill is a showcase of freshwater consumption reduction. Through the collaboration with Valmet, the mill has succeeded in reducing freshwater consumption from the target of less than 9.5 to less than nine m3 per air-dried tonne in the fiber line. Improving water efficiency and decreasing water consumption are also part of Valmet’s environmental targets for its own operations by 2030.
Disc filters play a crucial role in paper mills’ long circulation circuit, contributing to resource conservation and process efficiency. The key purposes of disc filters are not only fiber recovery but also water recovery for recirculation and water pollution prevention. More than 100 disc filters are in operation in India.
There are also two mills in India where water consumption has been reduced significantly with Valmet’s technology. To secure fiber supply and the viability of their board machine, the customer decided to integrate the mill with pulp production. They selected continuous G3 cooking technology from Valmet, which has proven its benefits through strong bleached hardwood kraft pulp and reduced energy, water, and chemical needs.
Disc filters play a crucial role in paper mills’ long circulation circuit, contributing to resource conservation and process efficiency. The key purposes of disc filters are not only fiber recovery but also water recovery for recirculation and water pollution prevention. More than 100 disc filters are in operation in India. In addition to supplying new disc filters, Valmet can upgrade the existing disc filters of any make to improve their efficiency.
Collaboration and Innovation
In developing new technologies for customers, Valmet strives to reduce freshwater consumption by implementing effective water recycling and treatment systems in customers’ mills, recovering and reusing evaporation and condensate water, and designing and manufacturing equipment that operates without water or with reduced water consumption.
To ensure the delivery of state-of-the-art water-efficient solutions and products, Valmet relies on its own R&D operations and close cooperation with customers, research institutes, and commercial partners.

“Valmet will collaborate with all pulp and paper mills around the world as long as we have competitive products and a solution to offer for the case. Threshold capacities differ by technology area, and in specific cases – for example, bioconversion – we can also offer smaller capacities like pilot plant scale. The initial check questions usually concern whether the company has valid environmental permits for the project. Local or global requirements are also checked. Our normal technology is considered to follow BAT, or best available technology,” explains Mr. Petri Paukkunen, Area President, Asia Pacific at Valmet.
“ We continuously innovate solutions and develop existing ones. Water efficiency is important for every mill today. Our customers have their targets set on a variety of levels, but all are improving their processes in some way. In general, it is water consumption that determines the effluent volume, and it can often be the effluent volume that motivates investments in water-efficient technology. As a supplier for this industry, Valmet can help our customers achieve their targets at every level, whatever they are. The technology to reduce water consumption and minimize mills’ water footprint already exists. It’s just a question of how much customers are willing to invest,” concludes Paukkunen.
Also Read: Advanced Effluent Recycling to Raw Water at Pulp and Paper Mills
It is also important to produce evaporation condensate that is so clean it can be 100 percent reused in the process and to avoid an unnecessary internal cooling system. Keeping the cooling and process water separate requires less chemical-treated water and leads to less spillage.
Sustainability and Circularity
Water is an essential part of pulp and paper production, which is gradually moving toward sustainability and circularity. This direction is also supported by local regulation and the global climate change and resource scarcity, technological innovation, and circular economy megatrends.
According to the Government of India’s Central Pollution Control Board guidelines, all paper mills in India must recycle water, and no effluent water is allowed to drain into nearby water bodies. Pulp and paper mills are advancing their reduction of water consumption. In practice, this includes shifting to technologies operating with reduced water consumption, implementing efficient strategies for water reuse, and introducing advanced effluent and process water treatment technologies to ensure water recirculation, good product quality, trouble-free runnability of processes, and compliance with environmental water discharge limits.



